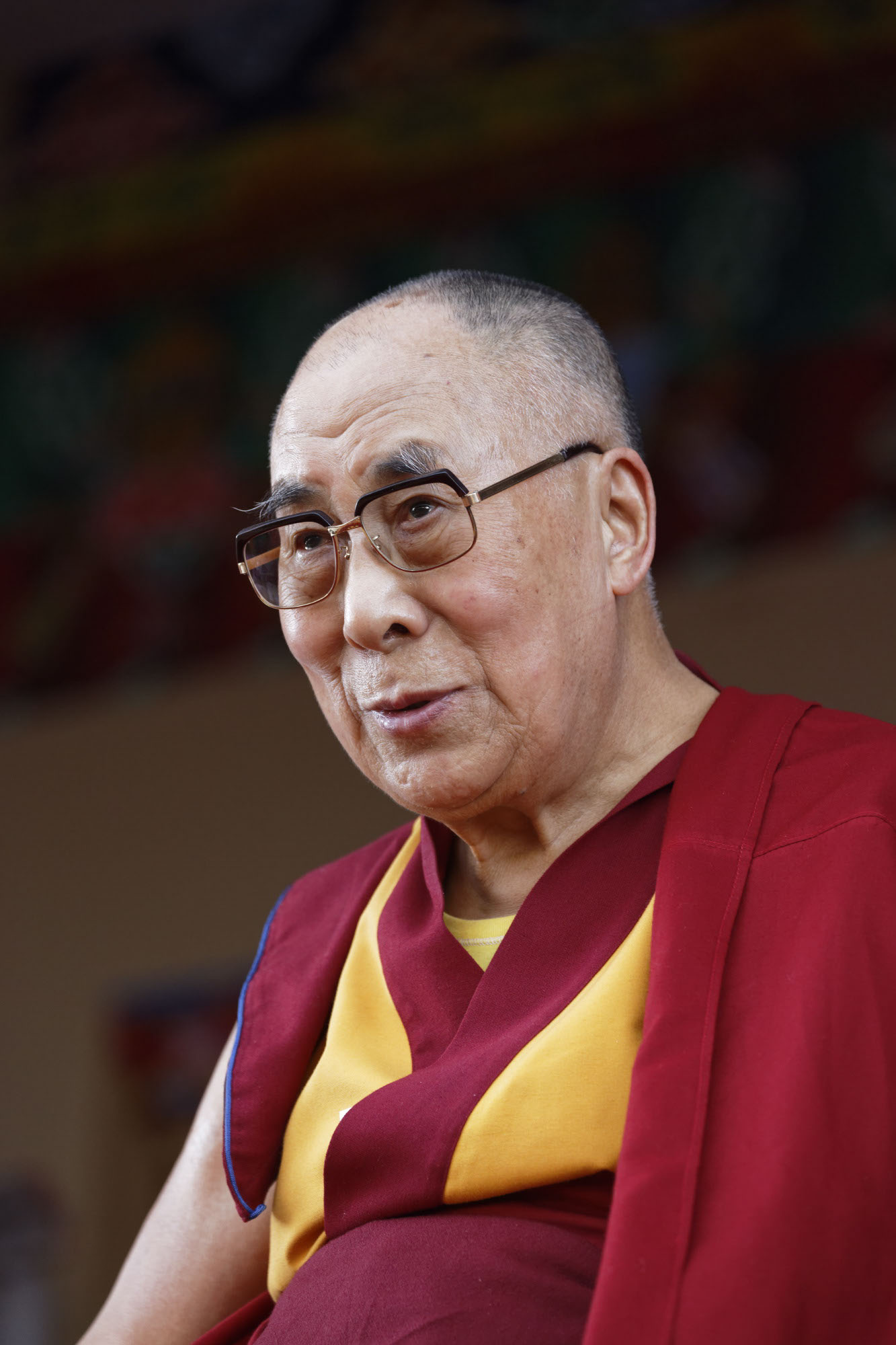
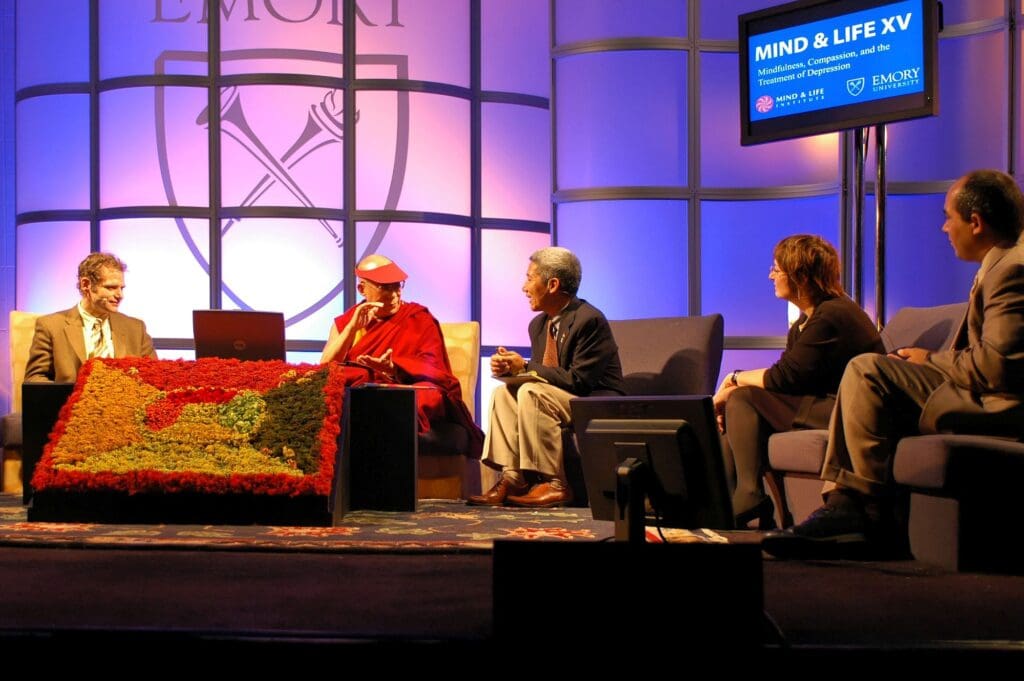
The Dalai Lama is a man of peace. He has consistently advocated policies of non-violence, even in the face of extreme aggression. He also became the first Nobel Laureate to be recognized for his concern for global environmental problems. He has travelled to more than 67 countries spanning six continents. He has received over 150 awards and honorary doctorates in recognition of his message of peace, non-violence, inter-religious understanding, universal responsibility and compassion. He has also authored or co-authored more than 110 books, including the “Book of Joy” with Archbishop Desmond Tutu.
The Dalai Lama, Tenzin Gyatso, was born on 6 July 1935 to a farming family in a small hamlet of Tibet. He is now the spiritual leader of Tibet, yet describes himself as a simple Buddhist monk. At the age of 23 he passed a rigorous examination with honors and was awarded the Geshe Lharampa degree, equivalent to the highest doctorate in Buddhist philosophy. In 1950, after China’s invasion of Tibet, he was called upon to assume full political power. Therefore, in 1954, he went to Beijing and met with Mao Zedong and other Chinese leaders. Five years later, following the brutal suppression of the Tibetan national uprising in Lhasa by Chinese troops, the Dalai Lama was forced to escape into exile. Since then he has been living in Dharamsala, northern India.
In 1963, he presented a draft democratic constitution for Tibet. The charter enshrines freedom of speech, belief, assembly and movement. It also provides detailed guidelines on the functioning of the Tibetan Administration with respect to Tibetans living in exile. In 1992, the Central Tibetan Administration published guidelines for the constitution of a future, free Tibet. In 1989 he was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize for his non-violent struggle for the liberation of Tibet.